By Layering One At A Time, 3D Printing Medical Implants Can Create A Physical Object From A Digital Design
 |
| 3D Printing Medical Implants |
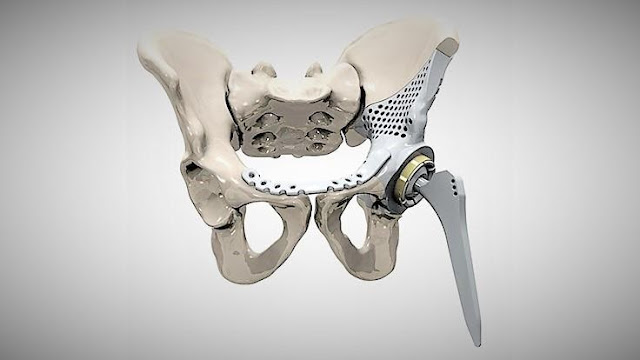
The term "3D Printed Medical Implants describes a technique that creates a real or physical object from a digital design by adding layers one at a time. The technology is in the early stages of development for healthcare applications and has great potential for a variety of uses in medical implants.With the aid of computer-aided design (CAD) or a magnetic resonance image (MRI), an artificial three-dimensional physical object is created using 3D printing technology. This object can be used to replace missing or damaged body parts, provide support, or repair biological structures that have been damaged. Dental bridges, acetabular hip implants, shoulder implants, and crowns for teeth are all examples of 3D printed medical implants.
Laser beam melting, electronic beam melting, droplet deposition, layered deposition, and two-photon polymerization are the main implant technologies used in 3d Printed Medical Implants. By melting and bonding at these locations with a powerful laser, 3D components are digitally sliced into 2D layers during the laser beam melting manufacturing process. Dental, orthopaedic, and craniomaxillofacial applications are among the many that are used by end-users like hospitals, surgery centres, pharmaceutical firms, biotechnology businesses, and medical institutes.
Manufacturers of medical devices use 3D printers to produce a variety of items, including ones with complex geometry or features unique to a patient's anatomy. A small batch of devices with a standard design are printed before multiple precise copies of the same gadget are made. Additional devices, referred to as patient-matched or patient-specific devices, are created using the patient-specific imaging data.
The simplicity of the printer's operation and the intended application of produced objects are just two of the factors that can affect the technology used for 3D printed medical implants. Powder bed fusion is the most widely used process for 3D Printed Medical Implants. This technique is applicable to a wide range of titanium and nylon parts used in medical equipment.
In 3D printing, actual objects are created from 3D digital files using a layer-by-layer additive technique. By supplying updated medical gadgets, this technology is anticipated to address the rising demands for sophisticated medical treatment. Additionally, it gives surgeons the ability to plan operations, which lowers the risks associated with complex procedures, infection risk, and anaesthetic exposure time. Furthermore, by permitting testing on 3D printed organs, this technique has completely changed preclinical drug testing.



Comments
Post a Comment