Circuit Breakers And Fuses Reduce And Control The Electrical Load On Equipment
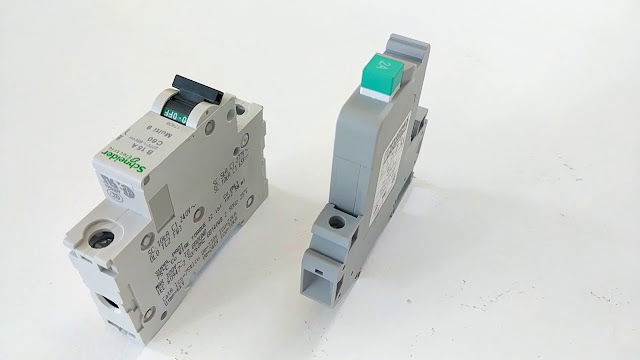 |
| Circuit Breakers And Fuses |
Breakers, Circuit Breakers and Fuses are
all intended to stop the flow of electricity. The fuse functions as a piece of
metal that melts when heated. Whereas an electrical fuse operates a shift
mechanism when an electrical overflow is detected.
Circuit
Breakers and Fuses are two types of electrical protection
devices commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Both
circuit breakers and fuses are designed to prevent electrical overloads, short
circuits, and other types of electrical faults that can lead to fires, damage
to electrical equipment, and even electrocution. However, there are some
important differences between circuit breakers and fuses that can affect their
suitability for different applications.
The Global Circuit Breaker And Fuses Market Is Estimated To Be Valued At US$ 17.7 Billion In 2021 And Is
Expected To Exhibit A CAGR Of 5.2% Over The Forecast Period (2021-2028).
we'll explore the basic principles behind circuit
breakers and fuses, their similarities and differences, and some factors to
consider when choosing between them.
Circuit breakers are electromechanical devices that
interrupt the flow of current in an electrical circuit when the current exceeds
a certain level, known as the circuit breaker's rated current. The basic
principle behind circuit breakers is that an electromagnet inside the breaker
becomes energized when the current exceeds the rated value, which causes a
switch to open and break the circuit. Circuit
Breakers and Fuses are available in a wide range of sizes and ratings, from
small devices that protect individual electrical outlets to large devices that
protect entire buildings.
One of the advantages of circuit breakers is that they
can be reset after they trip, meaning that they can be used multiple times.
This makes them a more convenient and cost-effective option than fuses, which
must be replaced each time they blow. Additionally, Circuit Breakers and Fuses can be designed to respond to different
types of faults, such as overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. This
allows them to provide more comprehensive protection against electrical
hazards.



Comments
Post a Comment